MAKE PROTECTION
YOUR SUPERPOWER

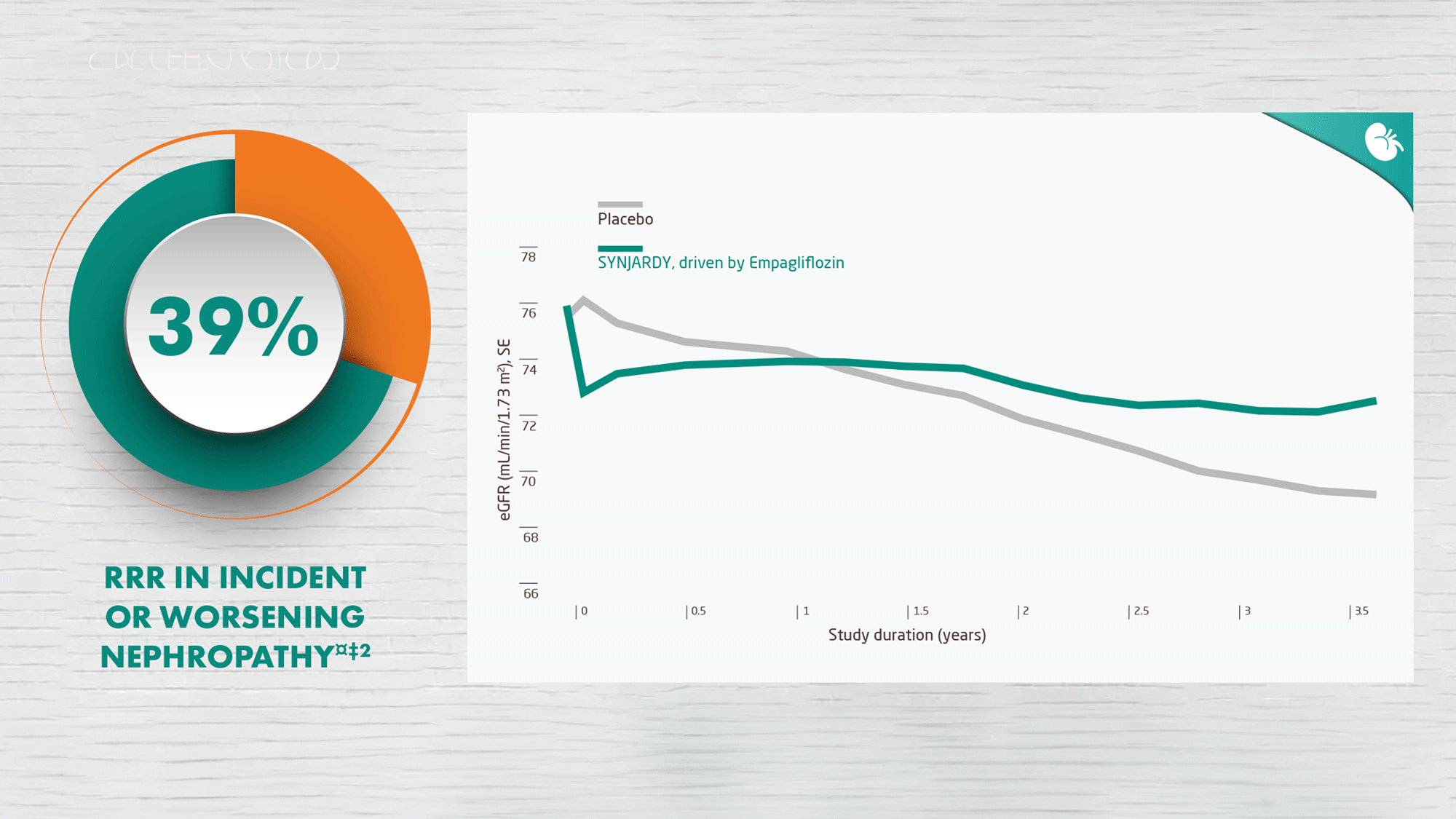
SYNJARDY®, driven by Empagliflozin maintained kidney function and reduced the risk of nephropathy€1,2
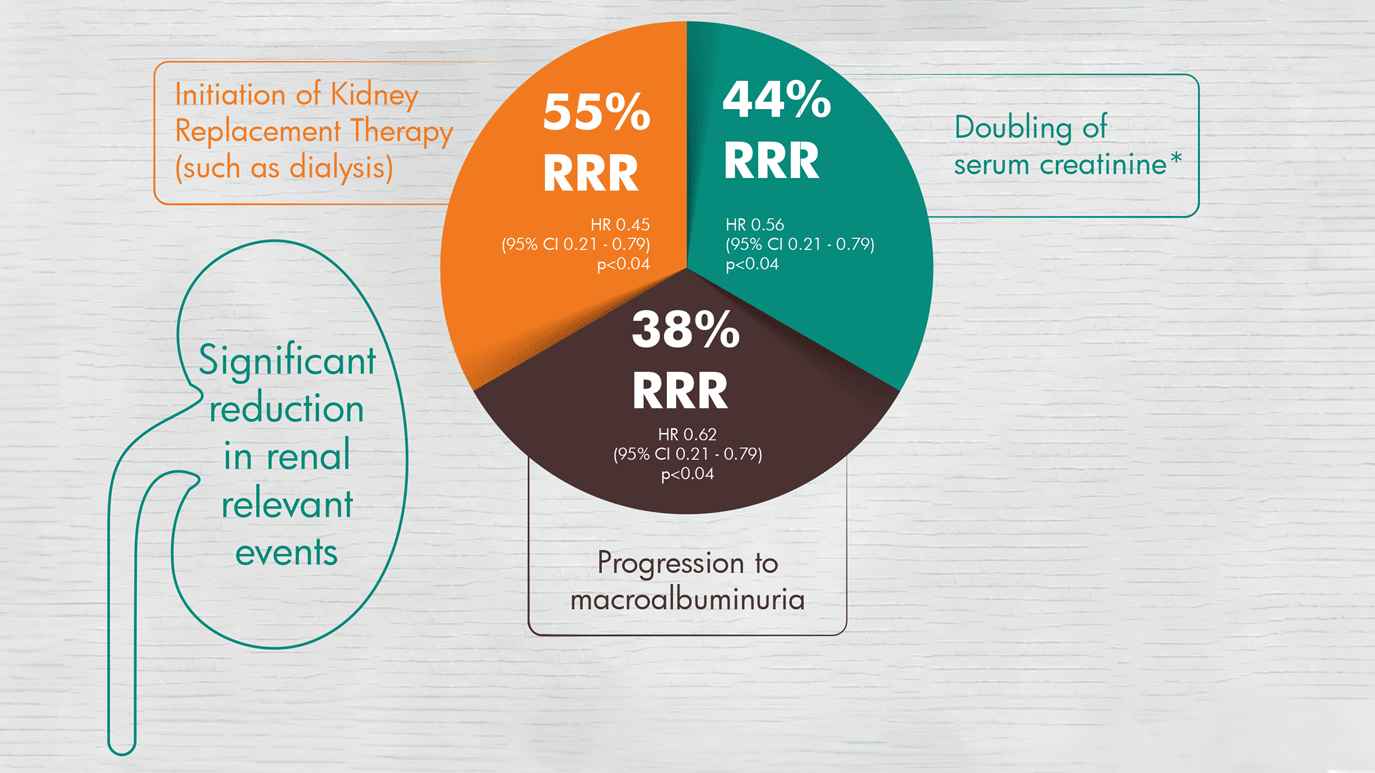
-
*
Adult patients with insufficiently controlled type 2 diabetes and CAD, PAD, or a history of MI or stroke.
-
¤
Incident or worsening nephropathy is defined as progression to macroalbuminuria, doubling of serum creatinine, eGFR of ≤45 mL/min/1.73 m2; initiation of renal replacement therapy; death from renal disease.
Incident or worsening nephropathy was a prespecified component of the secondary microvascular outcome in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. -
‡
Pooled data from 10 mg and 25 mg doses of Empagliflozin; both doses showed a comparable reduction in the risk of incident or worsening nephropathy.
References:
-
1.
Local SMPC Empagliflozin (Summary of Product Characteristics). May 2022
-
2.
Wanner C, Inzucchi S, Lachin J, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):323-334.
-
-
PC-AE-102256 | Expiry Date: 10/08/2026
