Optimized use of nursing time
Tenecteplase, compared to alteplase, may increase the efficiency of the nursing staff, due to reduced preparation time of the thrombolytic and reduced patient monitoring time.*5-6

Simpler patient transfer
With tenecteplase, patient transfer is simpler than with alteplase. Patients can be transferred immediately after receiving the IV bolus of tenecteplase, without the need for physician-supported medicalised transfer.†2

Efficiency supported by real-world evidence
In the treatment of AIS, the use of tenecteplase in real-world clinical practice led to reduced door-in-door-out (DIDO) and door-to-needle (DTN) times compared to alteplase.2 DIDO time, the time between arrival at first treating hospital and start of transfer for advanced post-IVT treatment in a secondary stroke center, was 22-minutes shorter with tenecteplase, compared to alteplase‡2. DTN time, the time between hospital arrival and IVT administration, was 6-minutes shorter with tenecteplase, compared to alteplase.§2
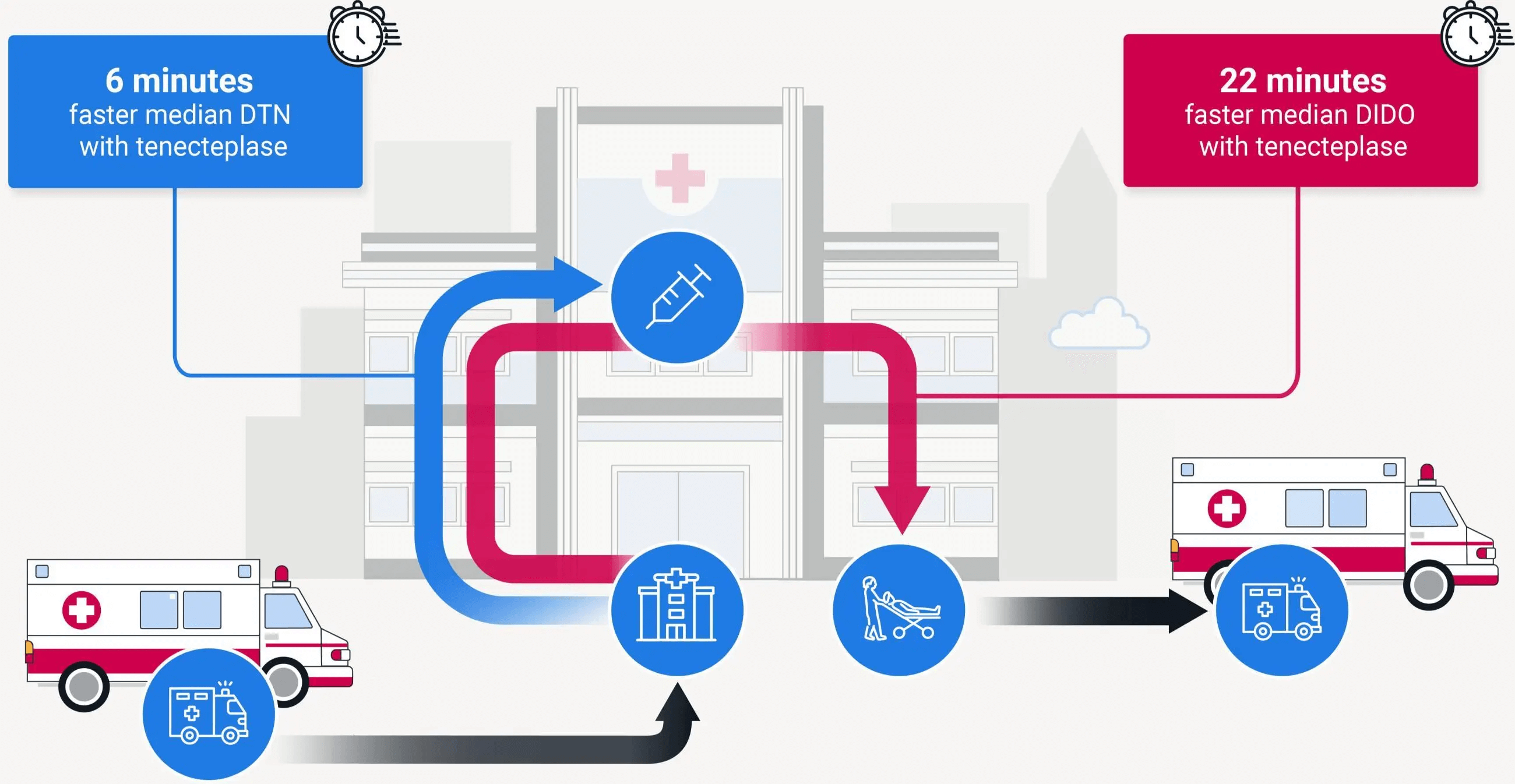
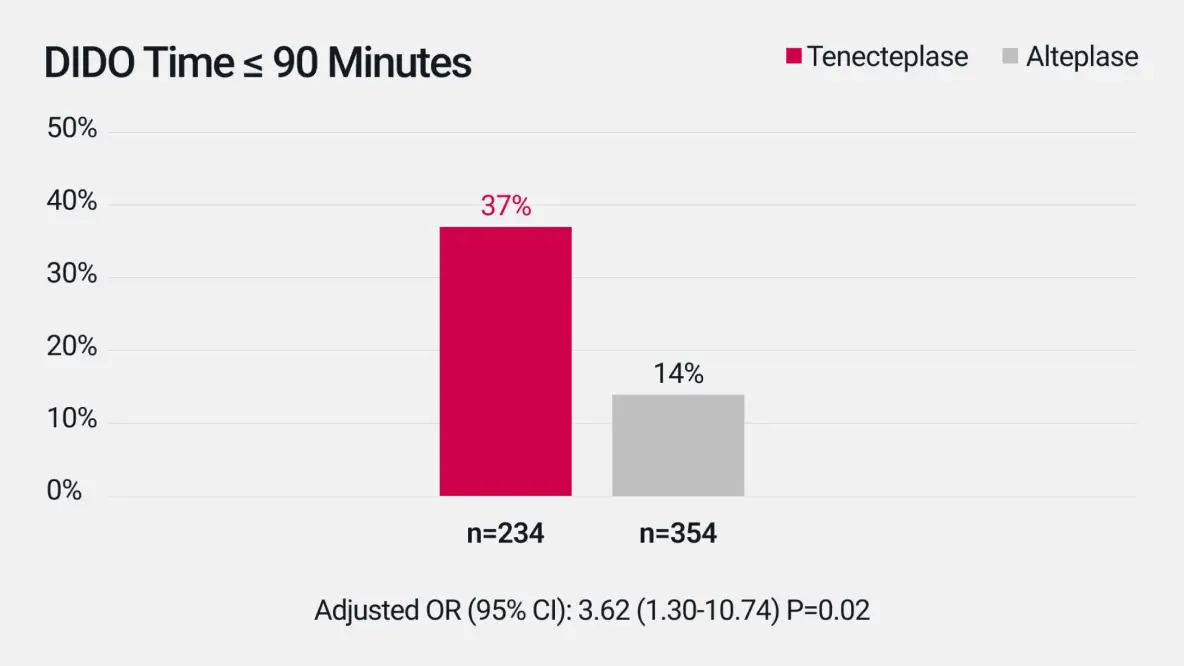
Door-In-Door-Out (DIDO) Time
Median DIDO was 113 min (IQR 83-153) for tenecteplase vs 135 min (IQR 100-177) for alteplase.‡2
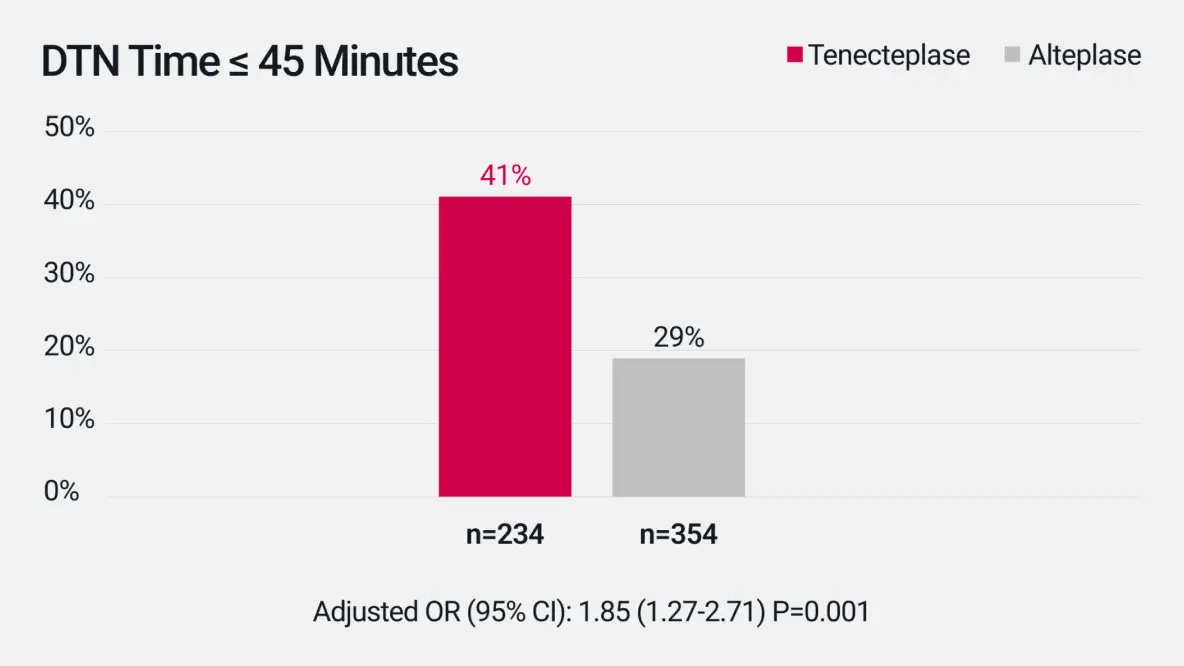
Door-to-Needle (DTN) Time
Median DTN was 51 min (IQR 38-80) for tenecteplase vs 57 min (IQR 43-75) for alteplase.§2
A systematic literature search and formal meta-analysis were conducted per PRISMA guidelines, adapted to noninferiority analysis. The primary outcome was freedom from disability (mRS score, 0–1) at 3-months, and additional efficacy and safety outcomes were analysed. The systematic search identified 5 trials enrolling 1585 patients (tenecteplase =828, alteplase=757). All alteplase patients received standard 0.9 mg/kg dosing, while tenecteplase dosing was 0.1 mg/kg in 6.8%, 0.25 mg/kg in 24.6%, and 0.4 mg/kg in 68.6% of participants.3
Footnotes
-
AIS: acute ischaemic stroke; CI: confidence interval; DIDO: door-in-door-out; DTN: door-to-needle; IQR: interquartile range; IV: intravenous; IVT: intravenous thrombolysis; OR: odds ratio
-
*
Refers to the amount of time needed for monitoring the patient actively during administration of the thrombolytic.5-6
-
†
Refers to the requirement for continuous monitoring of patients receiving thrombolytic infusion during transfer by trained and experienced physician.5-6
-
‡
DIDO was measured as the difference in the documented times from emergency department arrival at the treating hospital to discharge from that emergency department for transfer to another hospital for a higher level of care post thrombolysis, including but not limited to assessment for mechanical thrombectomy.2
-
§
DTN time was measured as the difference between the documented times of hospital arrival (or symptom discovery for inpatient stroke) and the thrombolytic bolus.2
References
-
1.
Metalyse® Summary of Product Characteristics, January 2024.
-
2.
Warach S.J. et al. Stroke 2022; 53:3583–3593.
-
3.
Mahawish K. et al. Stroke 2021; 52:e590-e593.
-
4.
Warach S.J. and Saver J.L. JAMA Neurol. 2020; 77(10):1203-1204.
-
5.
Menon B. K. et al. Lancet 2022; 400:161–169.
-
6.
Actilyse® Summary of Product Characteristics, March 2023.
PC-AE-102393 | Expiry Date: 02/18/2029

